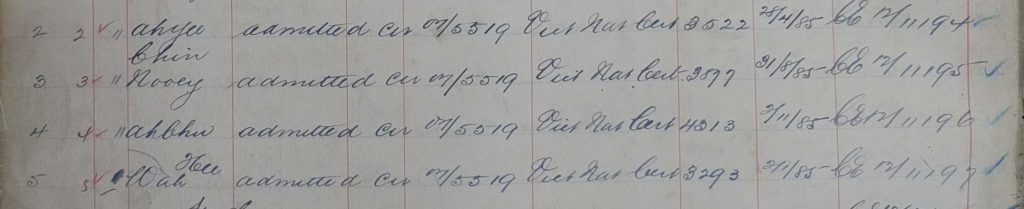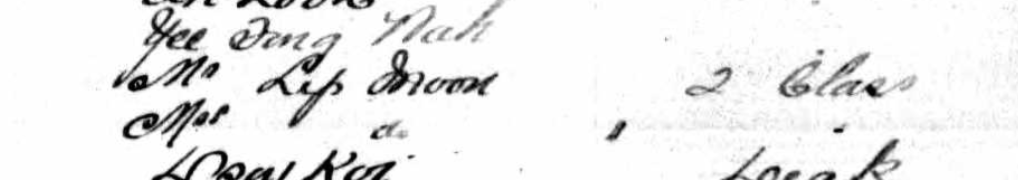By Sophie Couchman (Chinese Australian Family Historians of Victoria)
Searching through the Victorian CEDT Index you might find a few entries that do not contain information about the person with a lot of ‘n/a’ written in the fields. When you view the register page you will see ‘Issued under Circular 07/5519’ or words to that effect written across all the fields in the register.
I tried searching for these circulars in the National Archives of Australia without success. The NAA holds a lot of circulars! Chatting with Kate Bagnall about my problem she directed me to one of her blogposts and two registers related to the administration of the Immigration Restriction Act. Browsing through Kate’s images of the the register held in Adelaide in series AP214/9 I struck it lucky. Below is a copy of Circular 07/5519 which relates to the annotations in the Victorian CEDT registers.

[NAA: AP214/9, Photograph courtesy Kate Bagnall]
The body of the circular reads:
With reference to the re-admission to the Commonwealth of colored persons presenting Naturalization Papers, I have the honor to inform you that in cases where the Officer is satisfied that those person are the bona fide holders of such documents, they may be permitted to land on payment of the usual fee of £2 for a Certificate exempting them from the Dictation Test, which should be issued and cancelled immediately after their arrival. 2. The requirement of a fee in such cases will place the holders of Naturalization Papers on the same footing as other colored persons who have complied with the law and obtained certificates under the Immigration Restriction Acts prior to their departure from the Commonwealth. 3. I shall be glad if the necessary instructions can be issued, and advice sent to this Department from time to time of the admission of such persons and the payment of the fees in question.
From the date of this Circular, 12 June 1907, ‘colored persons’ travelling on their naturalization certificates had to pay a £2 fee in order to re-enter Australia. The same fee paid by those applying for a Certificate Exempting from the Dictation Test (CEDT). In other words the Australian government of the time was asking British subjects who were legally entitled to return to and live in Australia to pay a fee to exercise their legal right of return.
Unfortunately most of the entries for people who entered under the Circular only provide the name of the person making it difficult to match them with other records and confirm whether this person is your ancestor. However this information does mean that you should be possible to find naturalization records for these individuals.
If you want to find individuals who might have travelled under a Circular search the ‘Age’, ‘Occupation’ or ‘Residence’ fields of the Victorian CEDT Index for ‘n/a’ and then examine the digital photograph of the register page to see whether they travelled on a Circular.
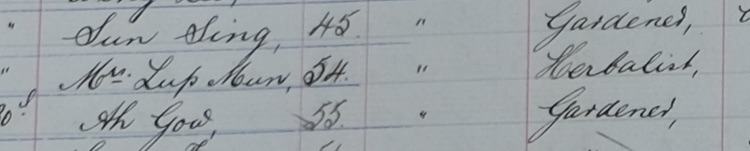
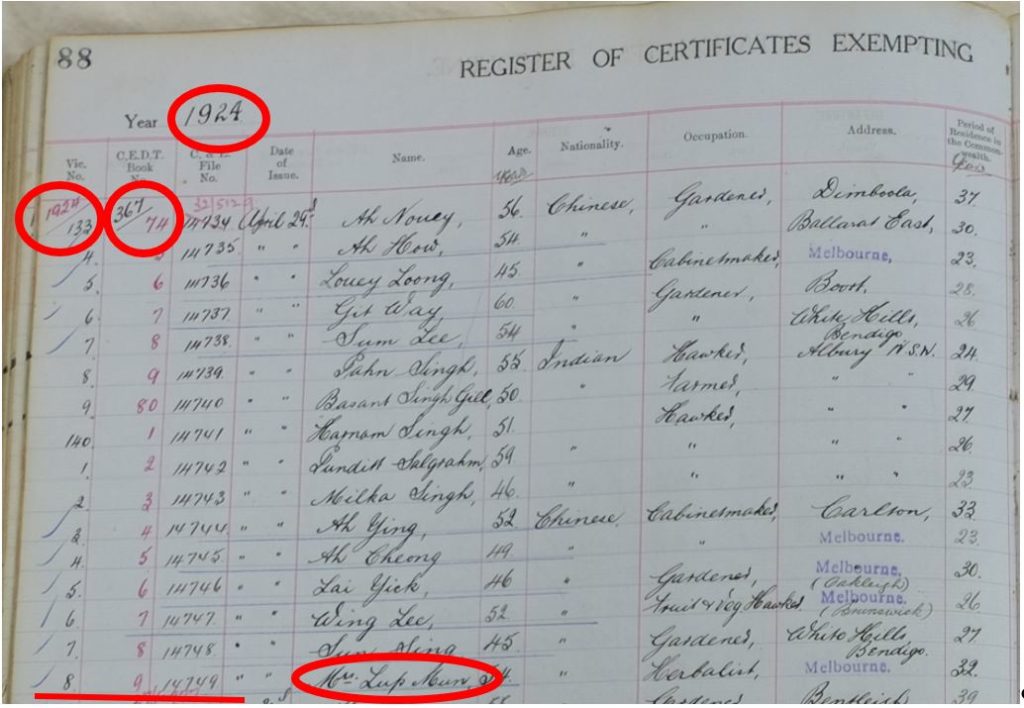
Here is the entry for Chin Nooey in the Victorian CEDT Index. It states that he entered Victoria on his naturalization certificate.

[Index entry for Chin Nooey, 1912, Register 1, p. 167, Victorian CEDT Index, http://cafhov.com/vic-cedt-index/?type=id&search=4157 (original data taken from ‘Register of Certificates Exempting from the Dictation Test, 1904–1914’, NAA: B6003, 1]
This particular entry in the register also provides the Victorian Naturalization Certificate number, 3177, and the date it was issued 31 August 1885. It also lists the C&E number 1912/11195 (which has unfortunately not survived culling). The Certificate number and date of issue are useful for searching for naturalization material and confirming that you have the correct person.
Searching NAA’s RecordSearch we find a file for ‘Chin Nooey’ in the A712 series. A712 files contain correspondence related to Naturalization applications and generally includes:
- A signed petition to the State Governor requesting naturalization under the Aliens Act, which might be approved or rejected
- An signed oath stating name, age, birth place, residence, occupation, years residence in Victoria
- A certificate signed by a warden, police magistrate or Justice of the Peace identifying the applicant and affirming that they are of ‘good repute’
- A file sheet with notes on the progression of the application with useful dates and numbers
[NAA: A712, C7618]
From Chin Nooey’s naturalization certificate we learn that his name is 陳女 (for some reason he writes the characters the English naming order with his family name second and not first). He was a 27 year old gardener who had arrived in Australia only four years earlier in 1881. Several ships in this year did not list individual Chinese who arrived so we cannot confirm that this was the year he arrived. Chin Chung, who the Justice of the Peace appears to have known certified to knowing Chin Nooey.
You need to check carefully to make sure each of these processes have been completed to be sure that the person was successfully naturalized. To ensure that the application was successful it is useful to search the ‘Index to Naturalization Certificates (1851-1922)’ held by the Public Records Office of Victoria (PROV 4396) (searchable on Ancestry.com) and the ‘Volumes of enrolled letters of naturalization’ (NAA: A727).

Certificate number 3877, issued 31 August 1885
[PROV: VPRS 4396, Index to Naturalization Certificates (1851–1922),
accessed via Ancestry.com]
A few additional things to note about the naturalization of ‘colored’, and particularly Chinese, people is that from 1885 the Victorian government made the decision to refuse all Chinese naturalization applications. This was not written into law but was made by administrative decision. Any applications after this date are unlikely to have been approved.
One of the reasons Chinese applied for naturalization between 1881 and 1885 was in order to travel freely under the Victorian Chinese Act 1881. It is therefore worth checking to see whether there is any outgoing travel shortly after a naturalization application as one of the reasons they may have been choosing to naturalize was to travel.
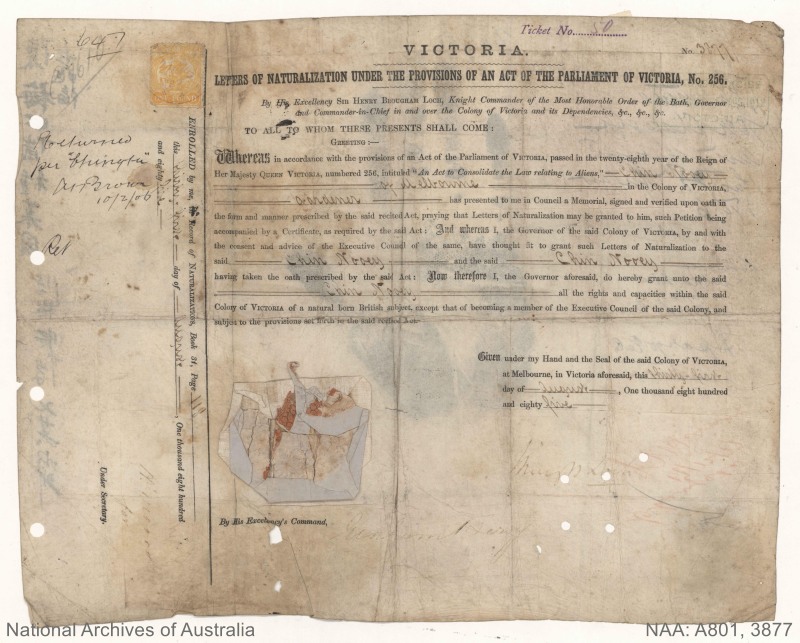
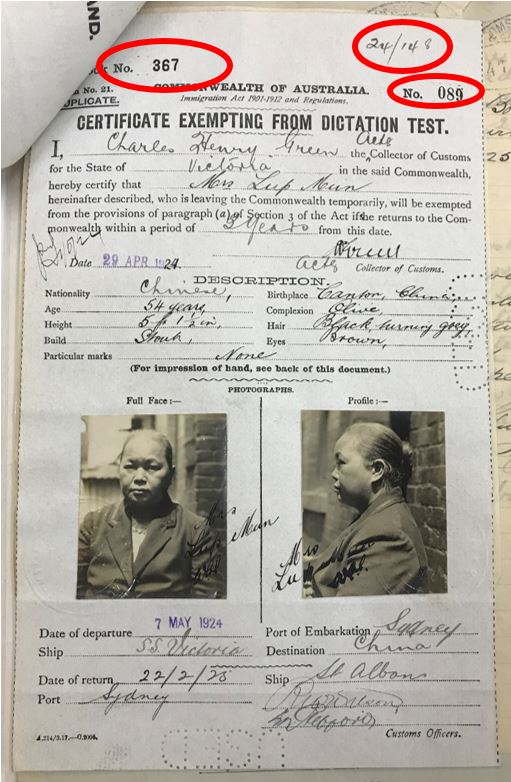
Both the Victorian and Federal governments were concerned about the fraudulent use of naturalization certificates by Chinese in order to travel. This resulted in a large number of naturalization certificates being cancelled. Series A801 contains these cancelled, confiscated and unclaimed certificates. Some of these certificates have photographs attached and written annotations on them detailing why they were cancelled. Chin Nooey’s was one of these cancelled naturalizations.
[NAA: A801, 3877]
Looking closely at the annotations on the certificate we can learn more about Chin Nooey and his travels. Official annotations in well-written Cantonese along the side of his certificate give his name as 陳梅 (which romanised using Yale Cantonese is Chan Muih). The character ‘陳’ is pronounced ‘Chin’ in Taishanese and Hakka. The character for the second part of Chin Nooey’s name sounds similar to 女 (Neuih), the name he writes himself. It has presumably been incorrectly written. The writing also indicates that he was a gardener (種菜园).
We can also see that Chin Nooey returned to Australia at the following times:
- 15 December 1887 on the Changsha
- 28 August 1896 on the Changsha
- 10 February 1906 on the Chingtu
- 1 July 1912 on the Nikko Maru
We can find Chin Nooey (often under different spellings) on incoming passenger lists in Victoria and New South Wales using this information but it has been more difficult to find when he left Australia which might be any time within three years of when he returned. He is likely to have departed from Victoria but also perhaps New South Wales or another Australian port.
One final piece of information that we know is that Chin Nooey’s naturalization certificate was confiscated or at the very least taken away from him. A search of Trove Newspapers shows that there were a four or five Chinese men (accounts vary) were arrested as prohibited immigrants when the Nikko Maru and the Aldenham arrived in Melbourne in July 1912. Three of these men took their cases to court – Ah You who arrived on the Aldenham claimed to be a a 53 year old gardener who had worked in Echuca and Bendigo, Ah Chong (or Ah Choong) claimed to be a tea hawker who had worked at Emerald Hill amongst other places and Laung Ah Choon (or Loon Ah Choon), claimed to be a 58 year old tea hawker but had worked in Carlton, Fitzroy and Richmond. All appeals were unsuccessful and they were charged with 6 months imprisonment, two with hard labour. Newspapers do not report the names of the other two (or one) person. Perhaps they chose not to go to court. Chin Nooey arrived on the same ship as Laung Ah Choon.

[‘”Returned Chinese”, Daily Telegraph, 26 July 1912, p.7 via Trove Newspapers, http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article238636804]
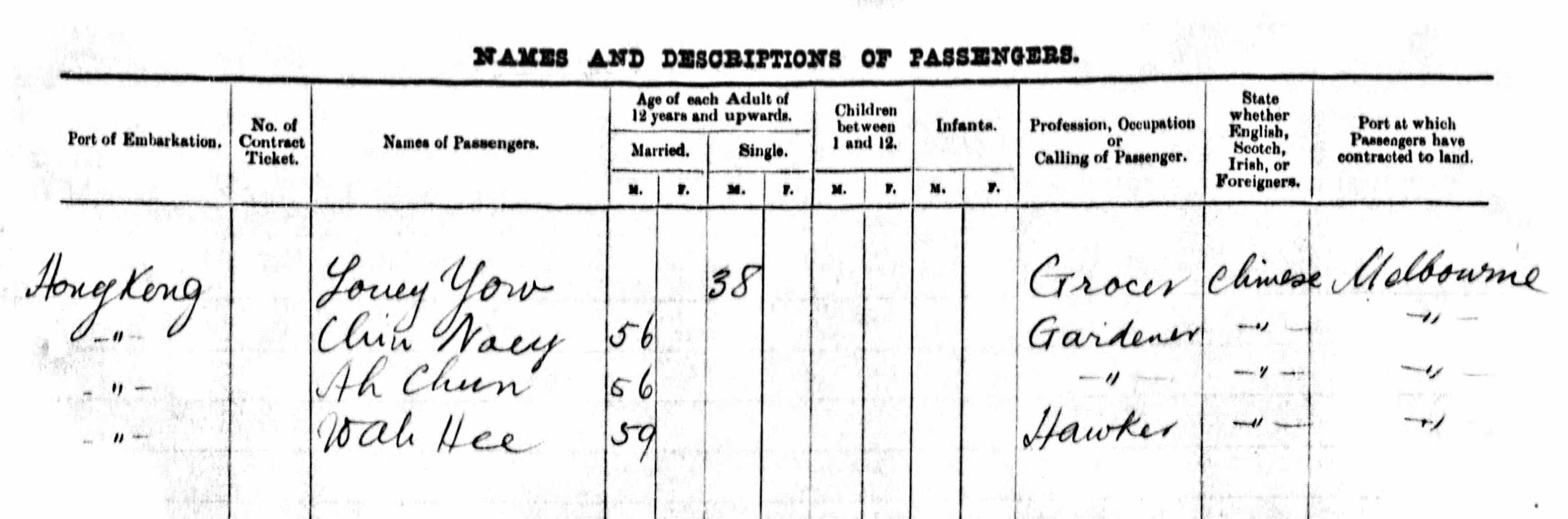
It is possible Chin Nooey was one of the men who did not go to court and remained unnamed in newspaper reports. If we got back to the Victorian CEDT Registers it is worth noting that they do specifically say that Chin Nooey was ‘admitted’ to Victoria. Laung Ah Choon’s name is not in the Registers and if we look at the names of the other men listed around Chin Nooey and compare them with the passenger lists for the Nikko Maru the two names following Chin Nooey’s name in the passenger list: Ah Chun and Wah Hee. These match the two following names in the Registers: Ah Chu and Wah Hee. I think perhaps these men’s naturalization certificates were most likely taken from them as part of checking their credentials, never returned or collected.
[PROV: Inward Overseas Passenger Lists (Foreign Ports), microfiche VPRS 7667, copy of VRPS 947, via Ancestry.com and NAA: B6033, 1, ‘Register of Certificates Exempting from the Dictation Test, 1904–1914’, via Victorian CEDT Index]
[Thanks to Dr Kate Bagnall for her feedback on this post]
Further reading
Aliens Statute 1865 (28 Vic No 256)
Chinese Act 1881 (45 Vic No 723)
Bagnall, Kate, ‘Chinese Australian families and the legacies of colonial naturalisation’, Tiger’s Mouth, http://chineseaustralia.org/legacies-of-colonial-naturalisation.
Dutton, David, Citizenship in Australia: A Guide of Commonwealth Government Records, National Archives of Australia, 2000
This post was last updated on 1 July 2021.